从 Kubernetes 1.22 开始,k8s 的容器运行是默认替换成 containerd。有必要深入了解 containerd 的内部实现原理。本篇通过分析 containerd 的代码深入理解其内部原理。
使用的版本为 containerd 1.5。
配置环境
下载 containerd 源码:
1
|
git clone github.com/containerd/containerd
|
启动 goland 的远程调试功能
入口
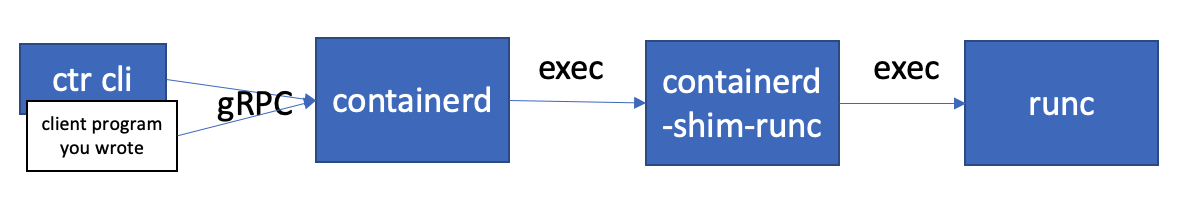
先来从 main 函数来看启动流程。从以下目录结构中可以看出来,containerd 项目目录中包含一个守护进程和对应的执行工具。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
cmd
├── containerd // containerd CRI 实现,对外提供容器服务,对内和 containerd-shim-runc 通讯
├── containerd-shim
├── containerd-shim-runc-v1 // 负责和 runc 通信,管理容器实例
├── containerd-shim-runc-v2 // v2 版本
├── containerd-stress
├── ctr // containerd 客户端命令行工具
├── gen-manpages
└── protoc-gen-gogoctrd
|
以下是它们之间的调用流程图:

containerd
containerd 本身是一个命令行工具实现,入口文件为 cmd/containerd/main.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
func main() {
app := command.App()
if err := app.Run(os.Args); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "containerd: %s\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}
|
command app
containerd 包含三个子命令:
configCommand: 输出 containerd 默认配置文件
publishCommand: 向 containerd 服务发布一个事件
ociHook: 启动一个 oci 钩子
app.Action 中定义了 containerd 的启动流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
...
app.Action = func(context *cli.Context) error {
...
// 加载配置文件
configPath := context.GlobalString("config")
...
// 通过配置文件创建 server,server 中包含 ttrpc、grpc、tcp、metrics
server, err := server.New(ctx, config)
...
...
// 启动 ttrpc 服务
serve(ctx, tl, server.ServeTTRPC)
...
if config.GRPC.TCPAddress != "" {
l, err := net.Listen("tcp", config.GRPC.TCPAddress)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to get listener for TCP grpc endpoint")
}
// 启动 tcp 服务
serve(ctx, l, server.ServeTCP)
}
...
// 启动 grpc 服务
serve(ctx, l, server.ServeGRPC)
...
return nil
}
...
|
再来看 server.New,它创建 containerd 服务:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
|
func New(ctx context.Context, config *srvconfig.Config) (*Server, error) {
...
// 从配置文件中加载插件
plugins, err := LoadPlugins(ctx, config)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
// 循环确认插件类型,并解析。
for _, p := range plugins {
id := p.URI()
reqID := id
if config.GetVersion() == 1 {
reqID = p.ID
}
log.G(ctx).WithField("type", p.Type).Infof("loading plugin %q...", id)
initContext := plugin.NewContext(
ctx,
p,
initialized,
config.Root,
config.State,
)
initContext.Events = s.events
initContext.Address = config.GRPC.Address
initContext.TTRPCAddress = config.TTRPC.Address
// load the plugin specific configuration if it is provided
if p.Config != nil {
pc, err := config.Decode(p)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
initContext.Config = pc
}
result := p.Init(initContext)
if err := initialized.Add(result); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "could not add plugin result to plugin set")
}
instance, err := result.Instance()
if err != nil {
if plugin.IsSkipPlugin(err) {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).WithField("type", p.Type).Infof("skip loading plugin %q...", id)
} else {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).Warnf("failed to load plugin %s", id)
}
if _, ok := required[reqID]; ok {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "load required plugin %s", id)
}
continue
}
delete(required, reqID)
// check for grpc services that should be registered with the server
if src, ok := instance.(plugin.Service); ok {
grpcServices = append(grpcServices, src)
}
if src, ok := instance.(plugin.TTRPCService); ok {
ttrpcServices = append(ttrpcServices, src)
}
if service, ok := instance.(plugin.TCPService); ok {
tcpServices = append(tcpServices, service)
}
s.plugins = append(s.plugins, result)
}
// 注册服务
// register services after all plugins have been initialized
for _, service := range grpcServices {
if err := service.Register(grpcServer); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
for _, service := range ttrpcServices {
if err := service.RegisterTTRPC(ttrpcServer); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
for _, service := range tcpServices {
if err := service.RegisterTCP(tcpServer); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
return s, nil
}
|
由此可知,containerd 中的服务都是通过插件加载的,插件的加载代码统一存放在 cmd/containerd/containerd 目录下的 builtins*.go 文件中。
其中包含以下几种服务:
- container
- content
- diff
- images
- events
- introspection
- leases
- namespaces
- snapshots
- tasks
- ttrpc
- version
具体的代码存放在 services 目录下,接下来我们来看 images 和 container 这两个最重要的服务。
镜像操作
containerd 作为 docker 的替代者,理所当然的需要实现 docker 的核心功能 OCI。images 服务包含:
- Get : 通过名称获取单个镜像
- List : 获取镜像列表
- Create : 创建一个镜像
- Update : 更新镜像
- Delete : 通过名称删除镜像
具体代码请看 services/images/local.go:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
// 初始化,注册成插件
func init() {
plugin.Register(&plugin.Registration{
Type: plugin.ServicePlugin, // 插件类型
ID: services.ImagesService, // 插件名称
Requires: []plugin.Type{
plugin.MetadataPlugin, // 依赖的插件
plugin.GCPlugin,
},
InitFn: func(ic *plugin.InitContext) (interface{}, error) { // 初始化方法
m, err := ic.Get(plugin.MetadataPlugin) // 获取 plugin.MetadataPlugin 插件,作为存储,内部使用 bblot 实现
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
g, err := ic.Get(plugin.GCPlugin) // GC 插件,用于资源回收
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &local{
store: metadata.NewImageStore(m.(*metadata.DB)),
publisher: ic.Events, // 内部的订阅发布模型
gc: g.(gcScheduler), // gc 调度器
}, nil
},
})
}
// images 服务的具体实现
type local struct {
store images.Store // 内部存储器
gc gcScheduler // gc 调度器
publisher events.Publisher // 内部的订阅发布模型
}
var _ imagesapi.ImagesClient = &local{}
...
|
这里我们可以把 images 的操作分为读取和修改两组。Get 和 List 为读取操作,就是从数据库中读取相关记录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
...
func (l *local) Get(ctx context.Context, req *imagesapi.GetImageRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*imagesapi.GetImageResponse, error) {
image, err := l.store.Get(ctx, req.Name)
if err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
imagepb := imageToProto(&image)
return &imagesapi.GetImageResponse{
Image: &imagepb,
}, nil
}
func (l *local) List(ctx context.Context, req *imagesapi.ListImagesRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*imagesapi.ListImagesResponse, error) {
images, err := l.store.List(ctx, req.Filters...)
if err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
return &imagesapi.ListImagesResponse{
Images: imagesToProto(images),
}, nil
}
...
|
Create、Update 和 Delete 是修改操作,核心是通过 events.Publisher 发布事件对应的事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// services/images/local.go
func (l *local) Create(ctx context.Context, req *imagesapi.CreateImageRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*imagesapi.CreateImageResponse, error) {
...
if err := l.publisher.Publish(ctx, "/images/create", &eventstypes.ImageCreate{
Name: resp.Image.Name,
Labels: resp.Image.Labels,
}); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
return &resp, nil
}
|
而真正处理该事件的订阅者则是 containerd 实现的 CRI 接口服务 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// pkg/cri/server/service.go
...
// criService implements CRIService.
type criService struct {
...
}
...
|
cri 启动时,订阅 containerd 事件,并启动事件处理协程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// pkg/cri/server/service.go
// Run starts the CRI service.
func (c *criService) Run() error {
logrus.Info("Start subscribing containerd event")
c.eventMonitor.subscribe(c.client)
...
// Start event handler.
logrus.Info("Start event monitor")
eventMonitorErrCh := c.eventMonitor.start()
...
}
|
eventMonitor.start() 内部处理逻辑如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
func (em *eventMonitor) start() <-chan error {
...
go func() {
defer close(errCh)
for {
select {
case e := <-em.ch:
logrus.Debugf("Received containerd event timestamp - %v, namespace - %q, topic - %q", e.Timestamp, e.Namespace, e.Topic)
if e.Namespace != constants.K8sContainerdNamespace {
logrus.Debugf("Ignoring events in namespace - %q", e.Namespace)
break
}
id, evt, err := convertEvent(e.Event)
if err != nil {
logrus.WithError(err).Errorf("Failed to convert event %+v", e)
break
}
if em.backOff.isInBackOff(id) {
logrus.Infof("Events for %q is in backoff, enqueue event %+v", id, evt)
em.backOff.enBackOff(id, evt)
break
}
if err := em.handleEvent(evt); err != nil {
logrus.WithError(err).Errorf("Failed to handle event %+v for %s", evt, id)
em.backOff.enBackOff(id, evt)
}
case err := <-em.errCh:
...
case <-backOffCheckCh:
...
}
}
}()
return errCh
}
|
namespace 不为 k8s.io 时事件都会被忽略。
criService 一共处理五类事件:
- TaskExit
- TaskOOM
- ImageCreate
- ImageUpdate
- ImageDelete
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// pkg/cri/server/event.go
// handleEvent handles a containerd event.
func (em *eventMonitor) handleEvent(any interface{}) error {
...
switch e := any.(type) {
case *eventtypes.TaskExit:
...
case *eventtypes.TaskOOM:
...
case *eventtypes.ImageCreate:
logrus.Infof("ImageCreate event %+v", e)
return em.c.updateImage(ctx, e.Name)
case *eventtypes.ImageUpdate:
logrus.Infof("ImageUpdate event %+v", e)
return em.c.updateImage(ctx, e.Name)
case *eventtypes.ImageDelete:
logrus.Infof("ImageDelete event %+v", e)
return em.c.updateImage(ctx, e.Name)
}
return nil
}
|
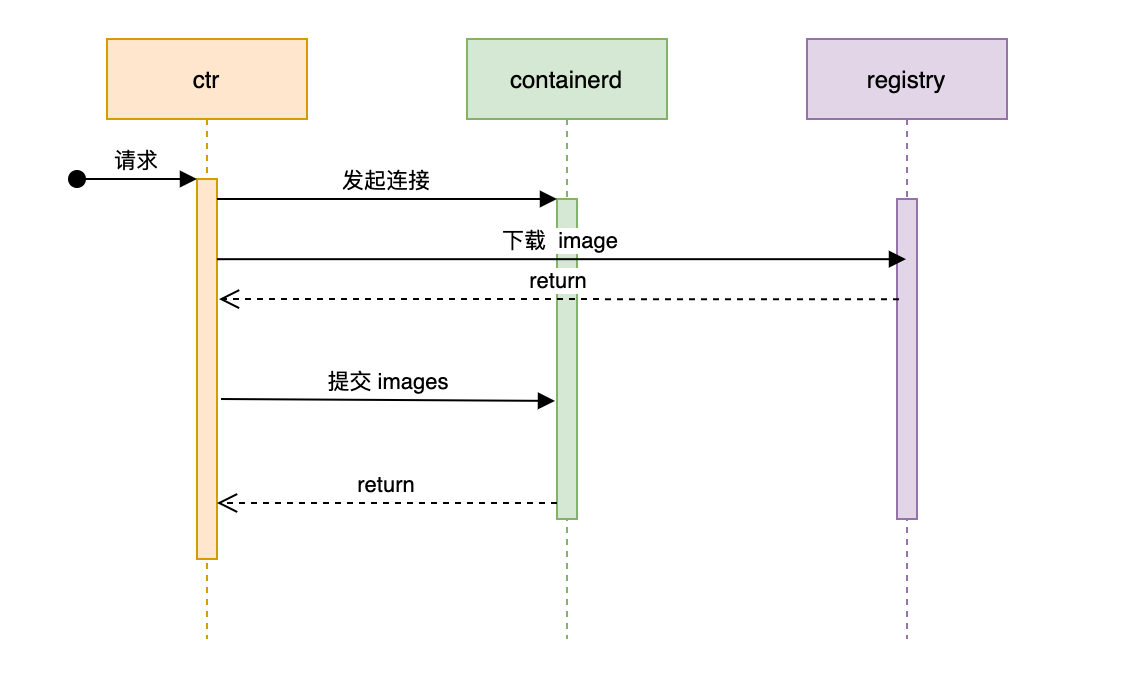
由此可知,Images 的后台操作都是调用一个处理方法 updateImage。
containerd 镜像完整的下载流程如下:

容器操作
介绍完镜像操作后,接下来就是关于容器部分的操作。以下我们通过一段代码来探究 containerd 内部的容器管理方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"syscall"
"github.com/containerd/containerd"
"github.com/containerd/containerd/cio"
"github.com/containerd/containerd/namespaces"
"github.com/containerd/containerd/oci"
)
func main() {
client, err := containerd.New("/run/containerd/containerd.sock", containerd.WithDefaultNamespace("default"))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer client.Close()
ctx := context.Background()
log.Println("get image")
img, err := client.GetImage(ctx, "docker.io/library/redis:alpine3.14")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Println("new container")
ctx = namespaces.WithNamespace(ctx, "default")
c, err := client.NewContainer(ctx, "redis",
containerd.WithNewSnapshot("redis-rootfs", img),
containerd.WithNewSpec(oci.WithImageConfig(img)),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("new container: %v", err)
}
defer c.Delete(ctx)
log.Println("new task")
task, err := c.NewTask(ctx, cio.NewCreator(cio.WithStdio))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
pid := task.Pid()
log.Printf("redis running in pid=%d\n", pid)
err = task.Start(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("start task: %v", err)
}
err = task.Kill(ctx, syscall.SIGINT)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("kill task: %v", err)
}
for {
status, _ := task.Status(ctx)
if status.Status == containerd.Stopped {
break
}
}
_, err = task.Delete(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("delete task: %v", err)
}
}
|
containerd 中创建一个容器之后,如果要运行这个容器,就需要创建一个 task 用来管理容器的生命周期。可以理解为 task 就是 containerd 的运行时。
创建
创建容器如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
// services/containers/local.go
func (l *local) Create(ctx context.Context, req *api.CreateContainerRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*api.CreateContainerResponse, error) {
var resp api.CreateContainerResponse
if err := l.withStoreUpdate(ctx, func(ctx context.Context) error {
container := containerFromProto(&req.Container)
created, err := l.Store.Create(ctx, container)
if err != nil {
return err
}
resp.Container = containerToProto(&created)
return nil
}); err != nil {
return &resp, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
if err := l.publisher.Publish(ctx, "/containers/create", &eventstypes.ContainerCreate{
ID: resp.Container.ID,
Image: resp.Container.Image,
Runtime: &eventstypes.ContainerCreate_Runtime{
Name: resp.Container.Runtime.Name,
Options: resp.Container.Runtime.Options,
},
}); err != nil {
return &resp, err
}
return &resp, nil
}
|
逻辑很简单,就是保存数据到内部存储中,再发布创建容器的事件。
启动
启动容器需要先创建一个 task,使用 task 来管理容器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
// services/tasks/local.go
...
func (l *local) Create(ctx context.Context, r *api.CreateTaskRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*api.CreateTaskResponse, error) {
...
// 创建容器运行时
c, err := rtime.Create(ctx, r.ContainerID, opts)
if err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
if err := l.monitor.Monitor(c); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "monitor task")
}
return &api.CreateTaskResponse{
ContainerID: r.ContainerID,
Pid: c.PID(),
}, nil
}
// runtime/v2/manager.go
// Create a new task
func (m *TaskManager) Create(ctx context.Context, id string, opts runtime.CreateOpts) (_ runtime.Task, retErr error) {
// 在磁盘上新建一个约束目录
bundle, err := NewBundle(ctx, m.root, m.state, id, opts.Spec.Value)
...
// 创建启动一个 containerd-shim-runc-v2 管理容器运行时
shim, err := m.startShim(ctx, bundle, id, opts)
...
// 创建一个 task
t, err := shim.Create(ctx, opts)
...
// 添加 task
if err := m.tasks.Add(ctx, t); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "failed to add task")
}
return t, nil
}
|
内部维护一个 TaskManager 来管理 tasks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
// runtime/v2/manager.go
// TaskManager manages v2 shim's and their tasks
type TaskManager struct {
root string
state string
containerdAddress string
containerdTTRPCAddress string
tasks *runtime.TaskList
events *exchange.Exchange
containers containers.Store
}
|
containerd 服务和 containerd-shim-runc-v2 使用 ttrpc 通讯。
停止
如何停止一个容器呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
// services/tasks/local.go
func (l *local) Kill(ctx context.Context, r *api.KillRequest, _ ...grpc.CallOption) (*ptypes.Empty, error) {
t, err := l.getTask(ctx, r.ContainerID)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
p := runtime.Process(t)
if r.ExecID != "" {
if p, err = t.Process(ctx, r.ExecID); err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
}
if err := p.Kill(ctx, r.Signal, r.All); err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
return empty, nil
}
// runtime/v2/shim.go
func (s *shim) Kill(ctx context.Context, signal uint32, all bool) error {
if _, err := s.task.Kill(ctx, &task.KillRequest{
ID: s.ID(),
Signal: signal,
All: all,
}); err != nil {
return errdefs.FromGRPC(err)
}
return nil
}
|
从 containerd tasks 服务中获取 tasks 信息,然后通过 ttrpc 连接 containerd-shim-runc-v2 并杀死进程。
containerd-shim-runc-v2 支持以下接口
- Create
- Delete
- Exec
- State
- Pause
- Resume
- Kill
- Pids
- CloseIO
- CheckPoint
- Update
- ResizePty
插件机制
containerd 内部服务都是通过插件方式注册。注册插件代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
// services/server/tasks/local.go
func init() {
plugin.Register(&plugin.Registration{
Type: plugin.ServicePlugin,
ID: services.TasksService,
Requires: tasksServiceRequires,
InitFn: initFunc,
})
timeout.Set(stateTimeout, 2*time.Second)
}
|
containerd 内部维护一个全局插件列表:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
// plugin/plugin.go
var register = struct {
sync.RWMutex
r []*Registration
}{}
|
对外提供三种方法:
- Load : 通过路径加载插件
- Register : 注册新的插件
- Graph : 遍历插件列表
注册的插件在 containerd 服务启动时初始化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
// services/server/server.go
// New creates and initializes a new containerd server
func New(ctx context.Context, config *srvconfig.Config) (*Server, error) {
...
for _, p := range plugins {
id := p.URI()
reqID := id
if config.GetVersion() == 1 {
reqID = p.ID
}
log.G(ctx).WithField("type", p.Type).Infof("loading plugin %q...", id)
// 新建插件上下文结构体
initContext := plugin.NewContext(
ctx,
p,
initialized,
config.Root,
config.State,
)
initContext.Events = s.events
initContext.Address = config.GRPC.Address
initContext.TTRPCAddress = config.TTRPC.Address
// 加载配置参数
if p.Config != nil {
pc, err := config.Decode(p)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
initContext.Config = pc
}
// 插件初始化
result := p.Init(initContext)
if err := initialized.Add(result); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "could not add plugin result to plugin set")
}
// 获取插件实例
instance, err := result.Instance()
if err != nil {
if plugin.IsSkipPlugin(err) {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).WithField("type", p.Type).Infof("skip loading plugin %q...", id)
} else {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).Warnf("failed to load plugin %s", id)
}
if _, ok := required[reqID]; ok {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "load required plugin %s", id)
}
continue
}
delete(required, reqID)
// 根据插件类型,加载成不同的服务
if src, ok := instance.(plugin.Service); ok {
grpcServices = append(grpcServices, src)
}
if src, ok := instance.(plugin.TTRPCService); ok {
ttrpcServices = append(ttrpcServices, src)
}
if service, ok := instance.(plugin.TCPService); ok {
tcpServices = append(tcpServices, service)
}
s.plugins = append(s.plugins, result)
}
...
return s, nil
}
|
插件初始化函数需要 InitContext。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// InitContext is used for plugin inititalization
type InitContext struct {
Context context.Context
Root string
State string
Config interface{}
Address string
TTRPCAddress string
Events *exchange.Exchange
Meta *Meta // plugins can fill in metadata at init.
plugins *Set
}
|
InitContext 中携带的 plugins 变量指向全局插件集合。结构体中保存插件初始化所需的参数,包括
- Root : containerd 项目的根目录,从配置文件中获取。(默认为 /var/lib/containerd)
- State : containerd 运行过程中数据的存放目录,从配置文件中获取,(默认为 /run/containerd)
- Config : 配置文件
- Address : gRPC 地址
- TTRPCAddress: ttrpc 地址
- Events: 全局的订阅发布模型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// plugin/context.go
// Plugin represents an initialized plugin, used with an init context.
type Plugin struct {
Registration *Registration // registration, as initialized
Config interface{} // config, as initialized
Meta *Meta
instance interface{}
err error // will be set if there was an error initializing the plugin
}
|
每个服务使用 Plugin 封装,插件的信息保存到 Registration 中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
// plugin/plugin.go
// Registration contains information for registering a plugin
type Registration struct {
// Type of the plugin
Type Type
// ID of the plugin
ID string
// Config specific to the plugin
Config interface{}
// Requires is a list of plugins that the registered plugin requires to be available
Requires []Type
// InitFn is called when initializing a plugin. The registration and
// context are passed in. The init function may modify the registration to
// add exports, capabilities and platform support declarations.
InitFn func(*InitContext) (interface{}, error)
// Disable the plugin from loading
Disable bool
}
|
Registration 包含插件类型,插件ID,配置参数,依赖的其他插件类型,初始化函数。